
In short, the answer is YES! As a Registered Dietitian, I believe that all foods can be part of a healthy diet, in sensible amounts. But there are actually different categories of processed foods, and some are better choices than others. Let’s break it down.
When you hear the term “processed foods”, you may automatically think of foods that come in a box or package. There’s more to the term “processed foods” though. Scientists at the School of Public Health at the University of Sao Paulo in Brazil developed a classification system called NOVA (it’s not an acronym) that groups foods into 4 different categories depending on the extent of the processing:
Unprocessed or Minimally Processed Foods:
Unprocessed foods have not undergone any changes whatsoever. Some examples are fresh fruit and veggies as well as plain unseasoned fish and meats. Minimally processed foods are essentially unprocessed foods that have been cleaned, dried, ground, pasteurized, fermented or frozen. No oils, fats, sugars, salt or other substances have been added to the original food. Dried fruit, frozen veggies, dried beans, dried herbs and ground spices are just a few examples of minimally processed foods. Both unprocessed and minimally processed foods should from the foundation of a healthy, balanced diet.
Processed Culinary Ingredients:
These are oils, fats, salt and sugars. These ingredients have been extracted from whole foods using processes such as pressing, grinding, refining and crushing. Vegetable oils for example are made from crushed seeds, nuts and fruit. Table sugar and molasses are obtained from sugarcane or sugar beet. Maple syrup is extracted from maple trees, and sea salt is mined from sea water.
Processed Foods:
These are unprocessed foods with added oils, fats, salt or sugars. Most processed foods have just 2 or 3 ingredients. Some examples are salted nuts, smoked fish, fruit packed in syrup, pickled veggies, and homemade / bakery-made bread. These foods can still be enjoyed as part of an overall healthy diet.
Ultra-processed Foods:
Most ready-to-eat and ready-to-heat products would be considered as ultra-processed foods. These are foods that are made by a series of processes and have extra ingredients such as additives, colours, flavours, emulsifiers, thickeners. Some examples are cake mixes, packaged pasta dishes, frozen entrées, reconstituted meat products and seasoned packaged snacks. While these foods can be convenient, enjoy them occasionally and in sensible amounts.
 On a recent trip to the grocery store, I noticed a brand of milk labelled as “high protein.” Compared to regular dairy milk, the high protein dairy milk contains 50% more protein and 50% less sugars. See the chart below for a quick nutritional comparison.
On a recent trip to the grocery store, I noticed a brand of milk labelled as “high protein.” Compared to regular dairy milk, the high protein dairy milk contains 50% more protein and 50% less sugars. See the chart below for a quick nutritional comparison.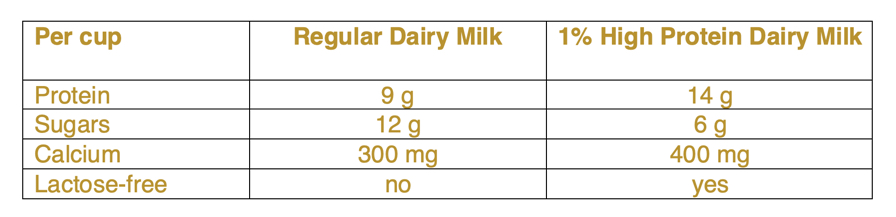 According to the company website (FairlifeCanada.ca), the high protein milk is made through an ultra-filtration process. No protein powders are added to the milk. Instead, the milk flows through multiple filters which concentrates the protein and calcium content while separating out the sugars (lactose). Most of the lactose is removed during this ultra-filtration. A lactase enzyme is then added to convert any remaining lactose into smaller, digestible sugars, resulting in a lactose-free milk with only 6 grams of sugars.
According to the company website (FairlifeCanada.ca), the high protein milk is made through an ultra-filtration process. No protein powders are added to the milk. Instead, the milk flows through multiple filters which concentrates the protein and calcium content while separating out the sugars (lactose). Most of the lactose is removed during this ultra-filtration. A lactase enzyme is then added to convert any remaining lactose into smaller, digestible sugars, resulting in a lactose-free milk with only 6 grams of sugars.





