This article originally appeared on Canadian Food Focus, and I received monetary compensation from them to research and write this information. My articles represent my personal and professional views. I am one of many dietitian writers for Canadian Food Focus, which is a source for Canadian food and farming stories that provide advice to help you make confident food choices.
You’re probably already familiar with the Nutrition Facts information found on the back of food packages. Health Canada is now introducing a new nutrition symbol that will appear on the front of food packages. This new front-of-package (FOP) nutrition symbol will help consumers quickly identify foods which are high in saturated fats, sugars and / or sodium. Here’s what you need to know.
Watch my national TV interview about Front of Package labelling.
Background
According to Heart and Stroke, 60% of the food we buy is prepackaged and processed, and many of these foods may be high in saturated fats, sugars and / or sodium. Eating a diet that’s high in these nutrients of concern is linked to a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes and some types of cancer. At the same time, 8 out of 10 Canadians say that nutrition is important when choosing foods.
To help Canadians make informed choices, Health Canada is introducing a new front-of-package (FOP) nutrition symbol to identify packaged foods which are high in saturated fats, sugars and / or sodium. The regulations came into effect on July 20, 2022 and food companies have until January 1, 2026 to update their packaging their labels. Over 40 countries including Chile, Argentina, Mexico and New Zealand, currently have a front-of-package nutrition labelling system.
What does the new front-of-package (FOP) symbol look like?


The new FOP symbol is a black and white image of a magnifying glass along with the name(s) of the nutrient(s) of concern – saturated fat, sugars and / or sodium – that are deemed high in the packaged food or beverage. It may appear either as a horizontal or vertical symbol. The FOP symbol may appear on the food package as one bilingual symbol or as two separate symbols in both official languages.


The FOP symbol will always appear on the upper right half of the food package. In the sample chocolate bar below, the symbol indicates that the food is high in saturated fat and sugars.
Which foods will need to show the FOP symbol?
For most packaged products, the definition of “high” means that the food or beverage contains 15% or more of the Daily Value for saturated fat or sugars and / or sodium per serving.
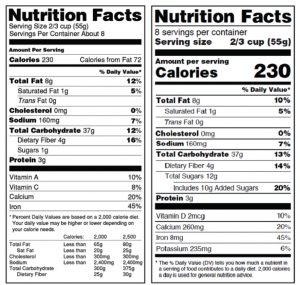
For example, take a look at the nutrition facts information below for a can of soup. The saturated fat is at 5% DV, the sugars is at 2% DV but the sodium is at 36% DV. So this soup would need to show the front-of-package nutrition symbol with the word sodium to let consumers know that this product is high in sodium.


Front-of-package symbol needed for the sample can of soup by January 1, 2026
For foods with a small serving size such as salad dressings or pickles, the criteria is 10% DV instead of 15% DV for saturated fat, sugars and sodium. And for pre-packaged main dishes that have a larger serving size, such as a frozen pizza or frozen lasagna, the criteria is 30% DV for those nutrients.
Which foods are exempted from the FOP symbol?
This is a list of some foods which are exempted either because of a recognized health benefit, technical or practical reasons.
- Plain fruits and vegetables
- Plain, unsweetened 2% milk & whole milk
- Plain cheese and yogurt*
- Plain nuts / seeds & nut / seed butter
- Eggs
- Raw, plain single ingredient meat, poultry & fish, including ground meat
- Butter, margarine, ghee; Vegetable oils; Sugar, honey, molasses, maple syrup; Salt (e.g. table salt, sea salt, Kosher salt, garlic salt, onion salt, celery salt, etc.) – It would simply be redundant and impractical to put a FOP symbol on these foods.
Any of the foods noted above are no longer exempt if they’re made with an ingredient that contains saturated fat, sugars and / or sodium. For example, a bag of plain salad is exempt from the FOP regulations. But is the bag of salad contains bacon bits and salad dressing, the FOP symbol may apply. Similarly, if salt is added to plain nuts, the FOP symbol may apply.
*Cheese and yogurt made from dairy these foods naturally contain saturated fat, sugars (lactose) and sodium (needed in the cheese-making process). However, these foods contain calcium which is considered a “shortfall nutrient” since many Canadians may not be getting enough and calcium. Any plain cheese or yogurt is only exempt from the FOP symbol if a serving of the food contains at least 15% DV for calcium (or at least 10% DV for calcium in foods with a serving size of 30 grams / 30 mL or less). The ongoing need for this exemption will be reassessed after 10 years.
Other exemptions include:
- Foods that are only sold at a farmer’s market, flea market, craft show, road-side stand or sugar bush by the person who prepared and processed the product
- Packaged individual portions of foods that are only intended to be served by a restaurant to accompany a meal or snack, such as coffee creamers or individually packaged crackers often served with soups at restaurants
- Foods sold in very small packages or with limited display space, such as milk, cream and goat’s milk which are sold in refillable glass containers since there available labelling space is limited to the lid
Pros and Cons
Pros: The FOP symbol will help consumers make informed food choices. In Chile, where a similar FOP labelling system has been in effect since 2016, 92% of consumers said that the FOP label influenced their food purchase. And overall household food purchases in Chile contained 37% less sodium and 27% less sugars.
Another pro is that this new nutrition labelling policy will inspire food companies to reformulate their products. In the next four years, expect to see new and improved products containing less saturated fat, sugars and sodium.
Cons: The FOP symbol could promote a “good food vs bad food” mentality which supports diet culture. Remember that we eat food for more than just nutrition. We eat food for celebration, comfort and connection.
Sue’s advice
Use the new FOP symbol as another tool to help you make informed choices. Read the Nutrition Facts table on the back of the package to see what other nutrients are offered in the food. Look at the ingredients list to determine whether any fat, sugars or sodium have been added to the product. If you happen to occasionally eat a food / beverage that has a FOP symbol, don’t feel guilty or ashamed. All foods can be enjoyed in moderation and fit into a healthy, balanced diet.